Portal:Aviation
| Main page | Categories & Main topics |
|
Tasks and Projects |
The Aviation Portal

Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. Aircraft includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships.
Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. (Full article...)
Selected article
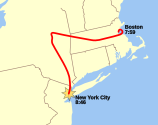
The aircraft crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center at 08:46 local time; the impact killed all 92 people aboard, including the hijackers. Many people in the streets witnessed the collision, and Jules Naudet captured the impact on video. News agencies began to report on the incident soon after and speculated that the crash had been an accident. The impact and subsequent fire caused the North Tower to collapse, which resulted in thousands of additional casualties. During the recovery effort at the World Trade Center site, workers recovered and identified dozens of remains from Flight 11 victims, but many other body fragments could not be identified. (Full article...)
Selected image
Did you know
...that the Vickers machine gun was the standard weapon on all British and French military aircraft after 1916?
- ...that the Bede BD-4 (pictured) was the first homebuilt aircraft to be offered in kit form?
...that the Silver Centenary biplane, built in Beverley, Western Australia in 1930, received its airworthiness certificate 77 years after its first flight?
General images -
In the news
- May 29: Austrian Airlines cancels Moscow-bound flight after Russia refuses a reroute outside Belarusian airspace
- August 8: Passenger flight crashes upon landing at Calicut airport in India
- June 4: Power firm helicopter strikes cables, crashes near Fairfield, California
- January 29: Former basketball player Kobe Bryant dies in helicopter crash, aged 41
- January 13: Iran admits downing Ukrainian jet, cites 'human error'
- January 10: Fire erupts in parking structure at Sola Airport, Norway
- October 27: US announces restrictions on flying to Cuba
- October 3: World War II era plane crashes in Connecticut, US, killing at least seven
- September 10: Nevada prop plane crash near Las Vegas leaves two dead, three injured
- August 6: French inventor Franky Zapata successfully crosses English Channel on jet-powered hoverboard
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Selected biography
Born in Mannheim, Wick joined the Luftwaffe in 1936 and was trained as a fighter pilot. He was assigned to Jagdgeschwader 2 "Richthofen" (JG 2—2nd Fighter Wing), and saw combat in the Battles of France and Britain. Promoted to Major in October 1940, he was given the position of Geschwaderkommodore (wing commander) of JG 2—the youngest in the Luftwaffe to hold this rank and position. He was shot down in the vicinity of the Isle of Wight on 28 November 1940 and posted as missing in action, presumed dead. By then he had been credited with destroying 56 enemy aircraft in aerial combat, making him the leading German fighter pilot at the time. Flying the Messerschmitt Bf 109, he claimed all of his victories against the Western Allies.
Selected Aircraft

The Airbus A380 is a double-deck, four-engined airliner manufactured by Airbus S.A.S. It first flew on 27 April 2005 from Toulouse–Blagnac Airport. Commercial flights began in late 2007 after months of testing, with the delivery of the first aircraft to launch customer Singapore Airlines. During much of its development phase, the aircraft was known as the Airbus A3XX, and the nickname Superjumbo has also become associated with the A380.
The A380 is double decked, with the upper deck extending along the entire length of the fuselage. This allows for a spacious cabin, with the A380 in standard three-class configuration to seat 555 people, up to maximum of 853 in full economy class configuration. Only one model of the A380 was available: The A380-800, the passenger model. It is the largest passenger airliner in the world superseding the Boeing 747. The other launch model, the A380-800F freighter, was canceled and did not join the ranks of the largest freight aircraft such as the Antonov An-225, An-124, and the C-5 Galaxy.
- Span: 79.8 m (261 ft 10 in)
- Length: 73 m (239 ft 6 in)
- Height: 24.1 m (79 ft 1 in)
- Engines: 4 * Rolls-Royce Trent 900 or Engine Alliance GP7200 (311 kN or 69,916 lbf)
- Cruising Speed: 0.85 Mach (approx 1,050 km/h or 652 mph or 567 kn)
- First Flight: 27 April 2005
- Number built: 254 (including 3 prototypes)
Today in Aviation
- 2013 – Nepal Airlines Flight 555, the de Havilland Canada DHC-6 Twin Otter 9N-ABO, skids off the runway at Jomsom Airport in Jomsom, Nepal, and falls 20 meters (65 feet) into the Gandaki River. All 21 people on board survive, but seven suffer serious injuries.
- 2011 – Launch: Space Shuttle Endeavour STS-134 at 12:56:28 UTC. Mission highlights: ISS assembly flight ULF6, ELC 3, ROEU, Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer. Final flight of Endeavour.
- 2001 – A Turkish Air Force CASA CN-235M-100 crashes into a field in Malatya, Turkey killing all 34 on board.
- 1995 – A Royal Air Force BAe Nimrod is forced to ditch in Moray Firth
- 1992 – STS-49, maiden flight of the Space Shuttle Endeavour lands at Edwards AFB.
- 1992 – Munich-Riem Airport, the main, international airport of Munich until is closed down. Operations moved to the new location near Freising. The IATA airport code MUC and the ICAO airport code EDDM were transferred to the new Munich Franz Josef Strauss Airport.
- 1992 – The 2,000th C-130 Hercules rolls off the production line.
- 1986 – Top Gun (film) opens in theaters in United States.
- 1977 – The landing gear failed on a New York Airways Sikorsky S-61 while it was taking on passengers on the roof of the Pan Am building. The aircraft rolled onto its side. Its spinning rotor blades killed four passengers waiting to board (including movie director Michael Findlay) and injured a fifth. Parts of a broken blade fell into the streets below, killing one pedestrian and injuring another.
- 1968 – A British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) Super Vickers VC10 on a routine service from Chicago and Montreal makes the airline’s first fully automatic approach and landing in London.
- 1961 – First flight of Mikoyan/Gurevich Ye-152/1, Soviet single-seat fighter/interceptor aircraft.
- 1959 – Newly-formed RCAF aerobatic team, the Golden Hawks, flying gold-finished North American F-86 Sabre, performed its first demonstration at Torbay, Newfoundland.
- 1958 – Captain Walter W. Irwin sets a new airspeed record of 1,404 mph (2,259 km/h) in a F-104 Starfighter, the first record over 2,000 km/h.
- 1957 – First flight of the Saunders-Roe SR.53, prototype interceptor aircraft of mixed jet and rocket propulsion developed for the Royal Air Force.
- 1954 – Birth of Dafydd Rhys "Dave" Williams, Canadian physician and a retired CSA astronaut. He had two space flights, both of which were Space Shuttle missions.
- 1953 – 90 U. S. Air Force Republic F-84 Thunderjets carry out a successful attack against Chusan, Korea.
- 1946 – A B-17G Flying Fortress crashes into White's Hill near Fairfax, California, while en route to Hamilton Field in Marin County, California, after running out of fuel. Two crew members are killed.
- 1945 – Birth of Brewster Hopkinson Shaw, Jr. former NASA astronaut, veteran of three space shuttle missions and has logged 533 hours of space flight. He was pilot of Space Shuttle Columbia in November 1983, commander of Space Shuttle Atlantis in November 1985 and commander of Space Shuttle Columbia in August 1989.
- 1945 – (16-17) British Pacific Fleet carrier aircraft strike Japanese airfields in the Sakishima Gunto.
- 1943 – Launch of Operation Chastise, attack on German dams by Royal Air Force No. 617 Squadron, subsequently known as the "Dambusters", using a specially developed "bouncing bomb" invented and developed by Barnes Wallis.
- 1942 – Canadian Pacific Airlines was formed.
- 1940 – Death of Allen Benjamin Angus, DFC, Canadian WWII fighter pilot and first Canadian ace of WWII.
- 1930 – First flight of the Blériot Bl-110 nicknamed 'Joseph Le Brix', French high wing single engine monoplane prototype designed for endurance records.
- 1929 – Wings, a silent film about World War I fighter pilots, is the first film, and the only silent film ever, to win the Academy Award for Best Picture.
- 1920 – Birth of Joseph Otis Fletcher, American Air Force pilot and polar researcher, first pilot to land at the North Pole along with William Pershing Benedict with a Douglas C-47 Skytrain.
- 1919 – A naval Curtiss aircraft NC-4 commanded by Albert Cushing Read leaves Trepassey, Newfoundland, for Lisbon via the Azores on the first transatlantic flight.
- 1918 – The Imperial German Navy recommissions the light cruiser Stuttgart after her conversion into a seaplane carrier. She is the only German seagoing aviation ship capable of working with the fleet commissioned during either World War I or World War II.
- 1917 – Death of Enrico Cottino and Francesco Guadalupi in their Farman 14.
- 1915 – (16-17 overnight) Two Royal Naval Air Service Avro 504s interceot the Imperial German Navy Zeppelins LZ 38 and LZ 39, badly damaging LZ39 with four 20-lb (9-kg) bombs dropped on its envelope from above.
- 1890 – Birth of http://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lucien_Bossoutrot, French pioneer aviator and politician.
References
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:Airplanes • P:AVIA