Portal:Aviation
| Main page | Categories & Main topics |
|
Tasks and Projects |
The Aviation Portal

Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. Aircraft includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot air balloons and airships.
Aviation began in the 18th century with the development of the hot air balloon, an apparatus capable of atmospheric displacement through buoyancy. Some of the most significant advancements in aviation technology came with the controlled gliding flying of Otto Lilienthal in 1896; then a large step in significance came with the construction of the first powered airplane by the Wright brothers in the early 1900s. Since that time, aviation has been technologically revolutionized by the introduction of the jet which permitted a major form of transport throughout the world. (Full article...)
Selected article
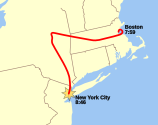
The aircraft crashed into the North Tower of the World Trade Center at 08:46 local time; the impact killed all 92 people aboard, including the hijackers. Many people in the streets witnessed the collision, and Jules Naudet captured the impact on video. News agencies began to report on the incident soon after and speculated that the crash had been an accident. The impact and subsequent fire caused the North Tower to collapse, which resulted in thousands of additional casualties. During the recovery effort at the World Trade Center site, workers recovered and identified dozens of remains from Flight 11 victims, but many other body fragments could not be identified. (Full article...)
Selected image
Did you know
...that a Fairchild C-119 Flying Boxcar was used in the 2004 film Flight of the Phoenix? ...that No. 112 Squadron RAF was the first unit from any air force to use the "Shark Mouth" logo on P-40 fighter planes? ... that Wing Commander John Lerew, ordered to defend Rabaul against Japanese invasion in 1942, signaled headquarters the legendary gladiatorial phrase "We who are about to die salute you"?
General images -
In the news
- May 29: Austrian Airlines cancels Moscow-bound flight after Russia refuses a reroute outside Belarusian airspace
- August 8: Passenger flight crashes upon landing at Calicut airport in India
- June 4: Power firm helicopter strikes cables, crashes near Fairfield, California
- January 29: Former basketball player Kobe Bryant dies in helicopter crash, aged 41
- January 13: Iran admits downing Ukrainian jet, cites 'human error'
- January 10: Fire erupts in parking structure at Sola Airport, Norway
- October 27: US announces restrictions on flying to Cuba
- October 3: World War II era plane crashes in Connecticut, US, killing at least seven
- September 10: Nevada prop plane crash near Las Vegas leaves two dead, three injured
- August 6: French inventor Franky Zapata successfully crosses English Channel on jet-powered hoverboard
Related portals
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Selected biography
Amy Johnson (1 July 1903 – 5 January 1941) C.B.E. was a pioneering British aviatrix.
Born in Kingston upon Hull, Johnson graduated from University of Sheffield with a Bachelor of Arts in economics. She was introduced to flying as a hobby, gaining a pilot's A Licence No. 1979 on 6 July 1929 at the London Aeroplane Club. In that same year, she became the first British woman to gain a ground engineer's C License.
Johnson achieved worldwide recognition when, in 1930, she became the first woman to fly solo from England to Australia. She left Croydon on 5 May of that year and landed in Darwin, Australia on 24 May after flying 11,000 miles. Her aircraft for this flight, a De Havilland Gipsy Moth (registration G-AAAH) named Jason, can still be seen in the Science Museum in London. She received the Harmon Trophy as well as a CBE in homage to this achievement, and was also honoured with the No. 1 civil pilot's licence under Australia's 1921 Air Navigation Regulations.
In July 1931, Johnson and her co-pilot Jack Humphreys became the first pilots to fly from London to Moscow in one day, completing the 1,760-mile journey in approximately 21 hours. From there, they continued across Siberia and on to Tokyo, setting a record time for flying from England to Japan. The flight was completed in a De Havilland Puss Moth.
Selected Aircraft

The Boeing 777 is a long-range, wide-body twin-engine jet airliner manufactured by Boeing Commercial Airplanes. It is the world's largest twinjet and is commonly referred to as the "Triple Seven". The aircraft has seating for over 300 passengers and has a range from 5,235 to 9,380 nautical miles (9,695 to 17,372 km) depending on model. Its distinguishing features include the largest diameter turbofan engines of any aircraft, six wheels on each main landing gear, a circular fuselage cross-section, and blade-shaped tail cone. Developed in consultation with eight major airlines, the 777 was designed to replace older wide-body airliners and bridge the capacity difference between the 767 and 747. As Boeing's first fly-by-wire airliner, it has computer mediated controls; it is also the first entirely computer-designed commercial aircraft.
The 777 is produced in two fuselage lengths. The original 777-200 model first entered service in 1995, followed by the extended range 777-200ER in 1997; the stretched 777-300, which is 33.3 ft (10.1 m) longer, began service in 1998. The longer-range 777-300ER and 777-200LR variants entered service in 2004 and 2006, respectively, while a freighter version, the 777F, debuted in 2008. Both longer-range versions and the freighter feature General Electric GE90 engines, as well as extended and raked wingtips. Other models are equipped with either the GE90, Pratt & Whitney PW4000, or Rolls-Royce Trent 800 engines. The 777-200LR ranks as the world's longest-range airliner and holds the record for longest distance flown by an unrefuelled commercial aircraft, with the demonstrated capability to fly more than halfway around the world.
United Airlines first placed the 777 into commercial airline service in 1995. As of August 2023, 1,716 777s have been delivered. The most common variant used worldwide is the 777-300ER, with 832 aircraft delivered, and Emirates operates the largest 777 fleet, with 134 aircraft (as of May 2019). The airliner has had 8 hull-loss accidents, with 541 fatalities. The most deadly incident was Malaysia Airlines Flight 17, in which a 777-200ER carrying 298 people was shot down by a missile over Ukraine on 17 July 2014.
Through the 21st century, the 777 has emerged as one of its manufacturer's best-selling models. Because of rising fuel costs, airlines have acquired the type as a comparatively fuel-efficient alternative to other wide-body jets and have increasingly used the aircraft on long-haul, transoceanic routes. Direct market competitors include the Airbus A330-300, the A340 and A350 XWB.
- Span: 212 ft 7 in (64.8 m)
- Length: 242 ft 4 in (73.9 m)
- Height: 61 ft 5 in (18.7 m)
- Engines: 2 X GE 90-115B
- Cruising speed: 0.84 Mach (555 mph, 892 km/h, 481 kn) at 35,000 ft (11,000 m) cruise altitude
- First flight: 12 June 1994
- Number built: 1,716 as of August 2023 (based on deliveries)
Today in Aviation
- 2012 – The Free Syrian Army reports that Syrian government attack helicopters have helped drive its forces out of the government' air defense base at Al-Ghantu, which they had briefly captured.[1]
- 2012 – A Kenya Police Eurocopter AS350 crashes on a hill in the Kibiku area of the Ngong Forest just outside Nairobi, Kenya, killing all six people on board. Among the fatalities are Kenya's Minister of Interior Security and likely presidential candidate George Saitoti and Assistant Minister of Interior Security Joshua Orwa Ojode.
- 2011 – Syrian government attack helicopters go into action during Syrian Army military operations against the rebel stronghold of Jisr ash-Shugur. The operations will conclude successfully on 12 June.
- 2011 – The Government of Norway announces that it will begin a gradual withdrawal of the six Royal Norwegian Air Force F-16 Fighting Falcons it has committed to Operation Unified Protector, the NATO intervention in the Libyan Civil War.[2]
- 2008 – Sudan Airways Flight 109, an Airbus A310, crashes at Khartoum International Airport and breaks apart, catching fire. 30 deaths are confirmed, 6 passengers are listed as missing.
- 1999 – Canadian CF-188 Hornets began Operation Joint Guardian during the Kosovo Air War.
- 1990 – British Airways Flight 5390, a BAC One-Eleven, suffers explosive decompression over Didcot, Oxfordshire, England when one of the front windscreen panes blows out. The captain is partially sucked out of the cockpit, but a flight attendant manages to keep his unconscious body from falling from the aircraft. The first officer lands the aircraft safely at Southampton Airport. All on board survive.
- 1989 – First female USAF test pilot. Capt Jacquelyn S Parker graduated from the Air Force Test Pilot School at Edwards AFB CA.
- 1987 – The Boeing Model 360 makes its first flight. The tandem rotored helicopter served as an Advanced Technology Demonstrator of many new design concepts.
- 1967 – First flight of the Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 prototype 23-11/1
- 1964 – First Lockheed XV-4A Hummingbird, 62-4503, (originally designated VZ-10) crashes, killing civilian Army test pilot. Aircraft had just transitioned from conventional to vertical flight at 3,000 feet (914 m) when control was lost. Airframe came down between Dobbins AFB and Woodstock, Georgia, injuring one civilian on ground.
- 1960 – Trans Australia Airlines Flight 538, a Fokker F-27, crashes into the ocean near Mackay, Queensland, Australia, killing all 29 on board in Australia's worst civilian air disaster. This crash was responsible for the mandatory installation of cockpit voice recorders in airliners in Australia, followed by the rest of the world.
- 1953 – The final experimental test flight for the turbojet powered #3 Douglas D-558-I Skystreak is flown by A. Scott Crossfield.
- 1944 – Flying from Italy carrying one 1,000-lb (454-kg) bomb each, 46 P-38 Lightning fighters of the U. S. Army Air Forces 82nd Fighter Group make a very-long-range fighter-bomber attack on the Romanian-American Oil Refinery at Ploesti, Romania. They destroy 23 German aircraft in exchange for the loss of 22 P-38 s.
- 1944 – RCAF fighter wings 144, 127 and 143 moved to France.
- 1943 – In one of the heaviest and most concentrated air attacks thus far in World War II, Allied aircraft drop 1,571 tons (1,425,202 kg) of bombs on Pantelleria.
- 1942 – An U. S. Army Air Forces LB-30 Liberator on a reconnaissance flight discovers that Japanese forces have occupied Kiska in the Aleutian Islands.
- 1936 – U.S. Navy Spartan NP-1, BuNo 3824, assigned at NAS Anacostia, Anacostia, D.C., ditches in the Back River, Virginia, after suffering engine failure following take-off from Langley Field, Virginia. Pilot J. Ware is KWF.
- 1919 – Ruth Law of the United States breaks the women’s altitude record, flying to 14,700 feet (4,481 m).
- 1913 – Marcel Brindejone des Moulinais wins the Pommeroy cup in Warsaw for the longest flight between sunrise and sunset, flying 900 miles from Paris.
- 1912 – The Austro-Hungarian submarine U-5 tows a kite balloon, apparently to determine the best coloration for submarines to avoid detection while underwater. Other than the experimental use of balloons from ships to bombard Venice in 1849 by its predecessor the Austrian Navy, it is the only operation of an observation balloon by the Austro-Hungarian Navy.
- 1908 – First flying club and civil airport established. Aeronautical Society chartered at New York City, and Morris Park air field established.
References
- ^ Solomon, Jay, and Nour Malad, "U.S. Bolsters Ties to Fighters in Syria," The Wall Street Journal, 13 June 2012 9:10 p.m. EDT.
- ^ "Libya Live Blog: Monday, August 1, 2011 – 16:56". Al Jazeera. 1 August 2011. Retrieved 2 September 2011.
- Shortcuts to this page: Portal:Airplanes • P:AVIA